When measurements must be ultra‑fast and perfectly deterministic, FPGAs shine. Unlike CPUs – whose performance depends on schedulers, caches, and interrupts – FPGAs have much more control over timing. They are hardware you can program: you “compile” logic into a network of computing elements on silicon, so your logic runs on the clock edges you specify. NI’s LabVIEW FPGA Module bridges the gap between gate‑level VLSI circuit design and productive engineering, letting you build high‑performance measurement solutions on platforms like CompactRIO (cRIO), FlexRIO, and R Series using a graphical workflow your team probably already knows.
This technical blog distills how and when to use FPGAs for custom measurements, the architectural patterns that actually work, and hard‑earned tips from DMC projects, plus links to DMC case studies and technical blogs you can reference as you architect your own system.
Why an FPGA for Measurement?
Determinism from microsecond to nanosecond scales
FPGA logic executes in hardware with clock‑accurate timing. On NI RIO targets, you can use single‑cycle timed loops (SCTLs) to run logic loops timed by clock signals that you specify. These loops have extremely low jitter, meaning that every iteration of the loop executes in the same amount of time. When you need very high confidence that control loops have a consistent time delta or that timestamps can be trusted, an FPGA may be the right tool.
Massive parallelism
Independent loops of logic on an FPGA execute in parallel. Unlike conventional CPUs, adding more loops to count edges, filter data, or implementing serial protocols won’t slow the other loops. This is ideal for multi‑sensor, mixed‑signal acquisition or protocol gateways.
Throughput without host bottlenecks
Stream continuous, high‑rate data using DMA FIFOs between FPGA and host, or bypass the host entirely with Peer‑to‑Peer (P2P) streaming between PXIe modules on the backplane. The FPGA can share data with oscilloscopes, waveform generators, vector signal analyzers, and more without burdening the host processor or memory.
Custom I/O and protocol timing
Implement custom digital front‑ends, encoders, counters, PWM, or proprietary serial timings that off‑the‑shelf DAQ devices don’t support. With CLIP and the IP Integration Node, you can also drop in HDL cores (VHDL/Verilog) or Xilinx IP where needed.
When to Choose an FPGA vs. PC or Real-Time (RT)?
Use this quick rule of thumb (derived from DMC best practices and NI documents):
- Choose FPGA when you require sub‑microsecond latency; hardware‑synchronous data paths; custom protocol waveforms; lossless streaming at hundreds of kS/s to GS/s; or multi‑loop parallel logic that must always meet timing.
- Choose RT (cRIO/PXI RT) when you need deterministic millisecond‑level control, supervisory logic, or file/logging tasks that coordinate with FPGA work. RT + FPGA is a common pairing.
- Choose PC when you need rich UIs, analytics, databases, or post‑processing, and timing isn’t safety‑critical. (Still pair with FPGA for preprocessing and rate reduction.)
DMC uses all three layers across industries (aerospace, electrification, advanced manufacturing), typically placing tight control and fast parallel logic on the FPGA, supervision and coordination on RT, and UX/data management on Windows. See our Real‑Time & FPGA overview and examples on DMC’s services page.
LabVIEW FPGA Essentials (what matters in practice)
Move data predictably:
Targets & clocks
Your LabVIEW project contains an FPGA target (cRIO chassis, FlexRIO, etc.) with base clocks (40 MHz onboard) and optional derived clocks. The top‑level clock governs logic outside SCTLs; SCTLs run in their selected clock domain. Use multiple clock domains to execute calculations at lower rates and fast I/O logic at higher rates.
DMA FIFOs
DMA FIFOs allow you to transfer data to and from the FPGA and host. The FIFO size can be scaled to avoid overflows. You can also create target‑scoped FIFOs to communicate between loops, but be sure to understand the different FIFO implementations.
Fixed‑point everywhere
Floating‑point math is expensive in FPGA fabric. Instead, you can do fixed‑point (FXP) math to be more hardware‑efficient. Controlled rounding and overflow modes and configurable word lengths & layouts allow you to plan for your specific algorithm. Prefer saturate where correctness is more important than speed, and wrap to optimize for resource usage. NI’s tables and guides are gold when sizing numeric types.
Bring your own HDL when needed
With CLIP (component‑level IP) or the IP Integration Node, you can insert vendor IP, legacy VHDL, or Xilinx IP cores into your own code to accelerate development.
Patterns DMC Reuses for High-Performance Measures
- Deterministic data capture and stream
Use the FPGA to capture signal edges with nanosecond resolution, decimate and filter the data on FPGA, stream features to RT/PC via DMA, and use the host system for logging, visualization, and analytics. We’ve applied this multi‑layered FPGA/RT/PC architecture on aerospace and defense systems with >500 channels. - Custom waveform synthesis at GS/s
With FlexRIO adapter modules, we’ve generated parameterized waveforms (delay/hold/ramp) at 1.25 GS/s using an adapter like the Active Technologies AT‑1212. Generating the waveforms on FPGA allows nanosecond‑level timing, great for optical/LIDAR, RF, and pulsed power. - Frequency‑domain triggers & inline RF analysis
Use P2P to stream digitizer data straight into an FPGA for windowing/FFT/mask comparison, then control backplane trigger lines to capture only events of interest. This eliminates host copies and makes “impossible” real‑time analyses practical. - High‑speed protocol emulation & HIL
The FPGA implements line‑speed channel models and packet timing, while PXI instruments handle I/O—use DMA for logging and P2P for cross‑module data paths. We’ve used this architecture in demanding hardware‑in‑the‑loop modem testing.
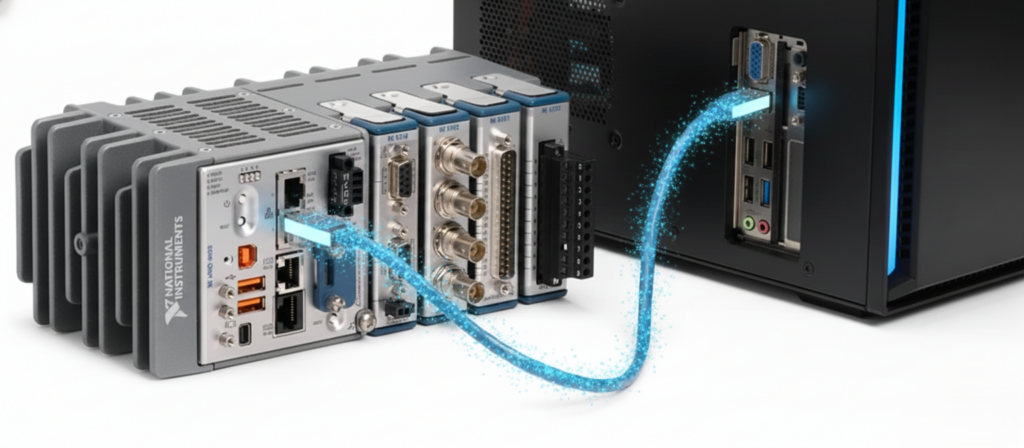

A Pragmatic LabVIEW FPGA Architecture
Keep the FPGA’s job small
Do the minimum required at hardware speed: time‑critical I/O, data reduction, protection, and lossless streaming. Push everything else to RT/PC. (This guideline is ubiquitous in DMC training decks.)
Use SCTLs wisely
SCTLs reduce resources and latency but increase timing pressure. Pipeline long combinatorial paths, separate fast and slow clocks, and avoid SCTL‑incompatible nodes (e.g., certain I/O or waiting functions).
Engineer your clocks
Start with the 40 MHz onboard clock and derive others only as needed. On FlexRIO, additional base clocks (100 MHz/200 MHz) and DRAM clocks are available; match clocking to I/O and algorithm needs.
Get data off the FPGA early
Choose target‑scoped FIFOs for on‑fabric communication and DMA FIFOs for host transfer. If you’re in a PXI(e) system and need device‑to‑device throughput or deterministic fan‑outs, configure P2P streams with NI‑P2P.
Choose numeric types deliberately
Pre‑size FXP to prevent overflow and use truncate where quantization error is tolerable.
Development & Debug Workflow that Saves Weeks
Simulate before you compile
FPGA builds can take minutes to hours. Use Simulated I/O and the FPGA Desktop Execution Node to build testbenches with simulated time, probe internal signals, and validate algorithms long before you commit to a hardware compile.
Layered testing
It’s a best practice to take a unit → component → system verification approach. Simulate units without I/O; component‑test clocked processes; then system‑test with real I/O or emulated streams.
Compile strategy
Use the FPGA Compile Cloud Service or a compile farm to parallelize big builds and keep engineers moving. NI’s developer center outlines your options.
Hardware Selection Notes
- cRIO: Rugged, modular C‑Series I/O; great for embedded measurements and deterministic control. Default 40 MHz FPGA clock; derive carrier clocks as needed.
- FlexRIO: PXI(e) FPGA with adapter modules for GS/s converters, custom front‑ends, and P2P; multiple base clocks; DRAM; ideal for inline DSP and RF/fast transients.
- R Series / Multifunction RIO: General‑purpose FPGA with direct DIO/AIO; useful when you need custom timing on classic DAQ channels.
- Other Platforms: If nothing above hits the mark, DMC can leverage our Embedded Services Team to develop a truly custom solution: FPGA Programming
If you’re unsure, DMC often starts with a short discovery mapping I/O timing, throughput, and latency to the simplest platform that meets the spec, escalating to FlexRIO only when rates, bandwidth, or P2P drive the need.
Real-World Examples & Further Reading
Top 5 FPGA-Related DMC Case Studies
Top 5 FPGA-Related DMC Blogs
- NI LabVIEW Part 1: Building Distributed and Synchronized FPGA Applications
Explains synchronization techniques for multiple FPGA chassis using NI 9469 modules. - NI LabVIEW Part 2: Synchronized Data Acquisition across Distributed FPGA Chassis
Discusses DMA FIFO strategies for transferring data between FPGA and RT targets in multi-chassis systems. - RT-301: Capabilities of Distributed LabVIEW Real-Time
The major benefits of running a Real-Time system are determinism and robust operation. - FPGA Programming Overview
A service-focused blog detailing FPGA programming capabilities, including Xilinx, Intel, and LabVIEW FPGA platforms. - Troubleshooting NTP with NI Hardware
While not purely FPGA, it’s relevant for time synchronization in FPGA-based DAQ systems.
A Starter Checklist for your FPGA Project
- Quantify timing: Required max latency, jitter, and timestamp resolution. If < 10 µs, you’re likely in FPGA territory.
- Estimate throughput: Peak and sustained rates; raw vs. reduced features; choose DMA vs. P2P accordingly.
- Partition the system: What must run in SCTLs? What can run in a slower clock? What can RT/PC do?
- Pick numeric formats: Fixed‑point widths, rounding/overflow policies; verify with simulation.
- Plan testbenches: Use Simulation (Simulated I/O) and the Desktop Execution Node before hardware compiles.
- Design streams & buffers: Size FIFOs to cover bursts of data and verify that underruns or overflows can’t occur in worst‑case scenarios.
How DMC Can Help
DMC has delivered deterministic, high‑throughput measurement systems across avionics, RF, electrification, and advanced manufacturing—often blending FPGA inline processing with RT coordination and PC‑level analytics and UX. Our team includes NI Certified LabVIEW Architects and deep FlexRIO/cRIO experience. Explore our Real‑Time/FPGA services and reach out—we’ll help right‑size your architecture and accelerate your first build.
Contact DMC today to learn more about our FPGA work or to discuss your specific requirements.